Conrad Peutinger II was born in 1475 in Augsburg, Germany. He was a humanist, scholar, and politician. His family was wealthy, giving him many chances to learn and grow.
He studied law and classical literature at Basel and Padua universities. He loved learning about the ancient world. This love made him famous for his work.
Peutinger is best known for the Tabula Peutingeriana, or Peutinger Map. It’s an old Roman map from the 4th or 5th century. He helped keep it safe and shared it with the world.
Early Life and Education of Conrad Peutinger II
Conrad Peutinger II was born in 1475 in Augsburg. He came from a wealthy family. This gave him a good education and chances to be involved in politics.
He went to universities in Basel and Padua. There, he studied law and classical literature. He learned about Renaissance humanism, which valued ancient texts.
Peutinger loved reading Cicero. Cicero’s ideas on speaking and being a good citizen inspired him. This shaped his interests and future work in the arts and culture.
Peutinger’s family and education were key. They helped him become a leading figure in the German Renaissance. He was shaped by humanist values and Renaissance education in the Augsburg patriciate.
Contributions to Humanism during the Renaissance
Conrad Peutinger II loved Renaissance humanism. He believed in education, reading old texts, and learning new things. He worked hard to keep and share ancient books with early printers.
He talked with famous thinkers like Erasmus of Rotterdam. They discussed big ideas like religion, philosophy, and spreading humanist values.
Peutinger was a key player in the humanist movement. He helped make Augsburg a place of learning, like the great cities of Italy. His work helped shape the culture of that time.
Peutinger worked very hard for the Renaissance humanist movement. He helped spread important ideas and made the time full of learning. His work inspires people who love to learn and read today.
Contributions to Geography and Cartography
Conrad Peutinger II made big contributions to geography and cartography in the Renaissance. He saved the Tabula Peutingeriana, an old Roman road map. This map showed Roman roads from the Atlantic to India.
This map was from the 4th or 5th century AD. It gave us a peek into the Roman Empire’s geography and roads.
Peutinger’s work on the Tabula Peutingeriana helped make detailed and accurate maps. These maps were key for the Renaissance’s exploration and science. His work helped us understand the world better and led to many discoveries.
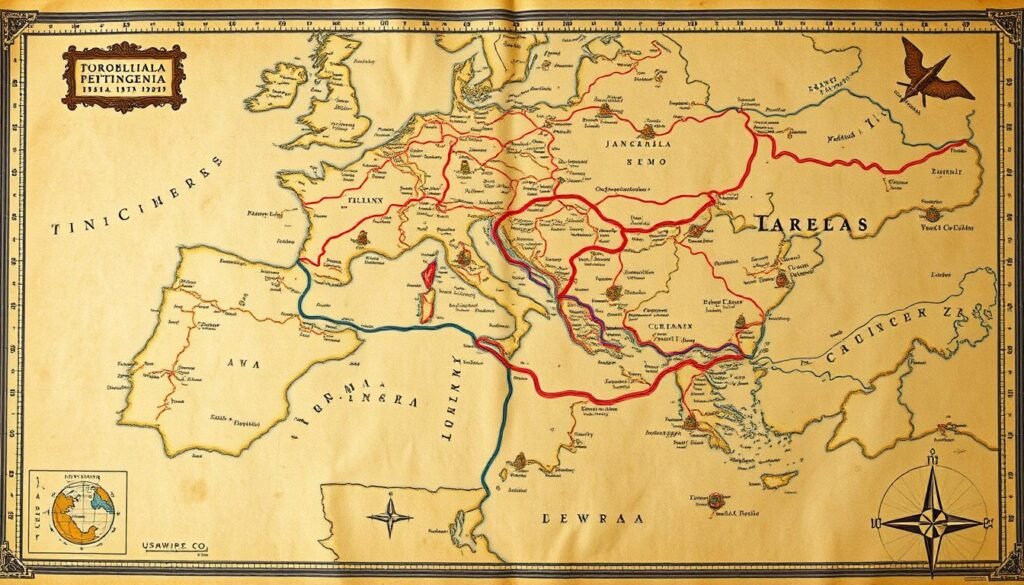
The Tabula Peutingeriana, a Roman road map, was very important for Peutinger’s work. He worked hard to save and study this ancient map. This helped shape the geography and science of his time.
The Impact of Conrad Peutinger II on the Arts and Culture
Conrad Peutinger II was a famous Renaissance humanist. He made a big impact on Augsburg’s arts and culture. He was a big supporter of the arts, making Augsburg as lively as Italian city-states.
Peutinger loved learning and keeping old knowledge alive. He worked with great artists like Albrecht Dürer. Together, they mixed art and learning. He also built big libraries for his many books and manuscripts.
Peutinger’s love for the arts and education made him a true Renaissance patron. His work helped make Augsburg known for its culture and arts. He left a lasting mark on the city.
The Relationship Between Science and Humanism
Conrad Peutinger II’s work showed how Renaissance science, humanist philosophy, and intellectual legacy came together. He kept the Peutinger Map alive, showing his love for real knowledge and maps that were right. Peutinger loved learning about old times but also liked science and thinking deeply.
His work helped others see the value of learning in a complete way. This way of learning was big in the Renaissance and later.
Peutinger loved old texts and maps, showing he cared about ancient wisdom. He also liked science, like the work of Hasan Ibn al-Haytham on light. This mix of old wisdom and new science was key to the Renaissance.
Peutinger’s work helps us see how Renaissance science, humanist philosophy, and learning evolved. He showed that science and old wisdom were connected. His work reminds us of the importance of learning in many ways.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Conrad Peutinger II
Conrad Peutinger II lived a life full of learning and helping others. He was a true Renaissance man. His work in politics, maps, and education is loved by scholars all over.
His famous map and other items are in museums. They show how much he helped keep history alive.
Peutinger loved old books and ideas. He changed European thinking a lot. He talked to big names like Erasmus and pushed for better schools.
Now, people all over value his work. His map and writings help us learn about the Roman Empire. They inspire new studies and discoveries.
Conrad Peutinger II’s spirit lives on. His love for learning and helping others is a lesson for us today.
